Search Results for: endothelial cells
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
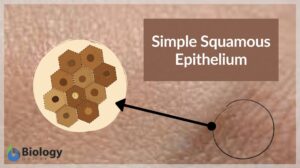
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
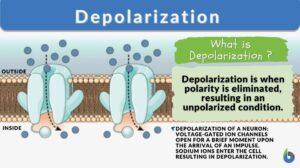
Depolarization
Depolarization is the removal of polarity by a process or action. It might also be used to describe how such activity leads... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Kupffer cell
Definition noun, plural: Kupffer cells A specialized stellate macrophage cell that is located fixedly within the liver... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Endothelial cells
Endothelial cell a thin, flattened cell, a layer of them lines the inside surfaces of body cavities, blood vessels, and... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Blood-brain barrier
Definition noun A semipermeable membrane that serves as a selective barrier separating the circulating blood and the... Read More
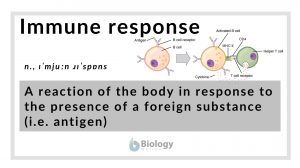
Immune response
Immune Response Definition An immune response is defined as the reaction of the body in response to the presence of a... Read More
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Endocytosis
Endocytosis Definition What is endocytosis in biology? Endocytosis is a cellular process by which a cell internalizes any... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
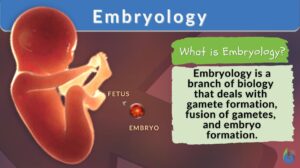
Embryology
Embryology Definition Embryology is a branch of biology that deals with the topics concerning gamete formation... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Mononuclear phagocyte system
Definition noun A system of cells located in reticular connective tissue, and are associated primarily with phagocytosis and... Read More
Lymph nodes
Lymph nodes definition Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs located in different parts of the body and act as... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Intermediate filaments
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Prostacyclin
Definition noun, plural: prostacyclins Any member from the subfamily of eicosanoids, with a chemical formula of C20H32O5,... Read More
Lymph capillary
Definition noun, plural: lymphatic capillaries (anatomy) A minute, thin-walled vessel of the lymphatic system that is... Read More
Bradykinin
Definition noun A nonapeptide that is vasoactive causing blood vessels to dilate Supplement Bradykinin is a type of kinin.... Read More
Cell recognition
Definition noun (1) Mutual recognition between cells, usually by specific complementary interaction between their respective... Read More
Lymph glands
Lymph gland --> lymph node (Science: anatomy) small bean-shaped organ made up of a loose meshwork of reticular tissue in... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Capillary permeability
Definition noun The property or capability of capillary walls to allow the selective flow of substances and cells into and... Read More